Anemia prevalence nears 40% in India
Anemia is a condition in which a person lacks sufficient healthy hemoglobin, the substance carrying oxygen in red blood cells.
This disease is very common, and can result in the person feeling tired, weak, dizzy, and short of breath. GlobalData’s epidemiological analysis of anemia found that the disease burden varies significantly by country and is quite common even in developed countries.
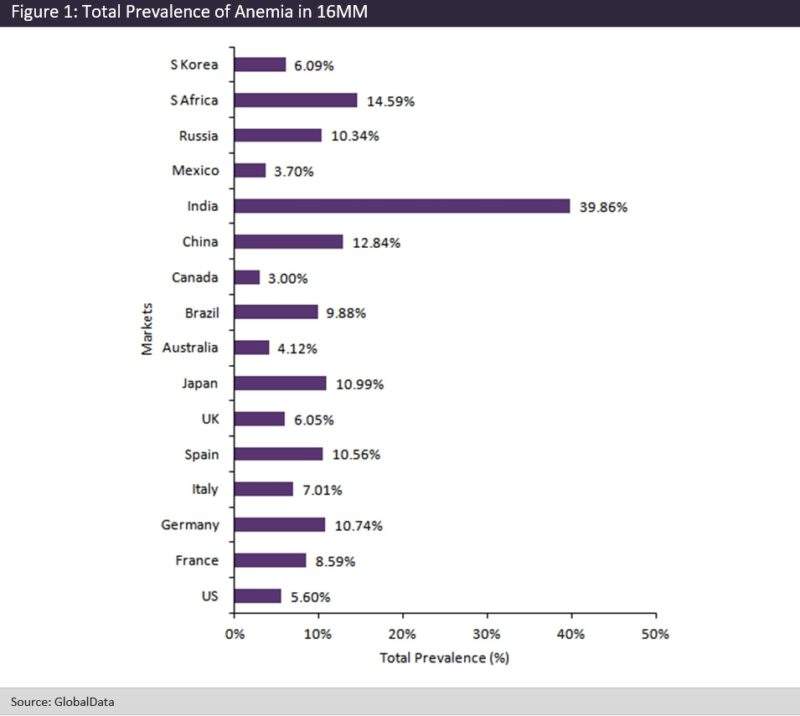
GlobalData epidemiologists analyzed the literature to determine the total prevalence of anemia in the 16 major pharmaceutical markets (16MM: US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK, Japan, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, India, Mexico, Russia, South Africa, and South Korea). Total prevalence is defined as including both diagnosed and undiagnosed cases. GlobalData epidemiologists obtained data from studies that collected blood samples from the general populations and tested them for hemoglobin levels. Anemia is defined as having a hemoglobin levels below the thresholds set for specific age groups by the World Health Organization (WHO). The figure below presents the total prevalence of anemia in the 16MM. India has the highest total prevalence of anemia at 39.86%, while Canada has the lowest at 3%. The US and 5EU (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK) have total prevalence levels ranging between 5.6–10.74%, making the disease a common occurrence in these markets.

Anemia has many different causes, including sickle cell anemia, iron-deficiency anemia, or anemia brought on by other health conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypothyroidism. Iron-deficiency anemia is the most common form, making up about 50% of all anemia cases. The majority of anemia can be treated relatively easily and can be prevented by a balanced healthy diet. But why is there still such high prevalence of anemia in the 16MM, even within the developed markets?
India has the highest prevalence of anemia among the 16MM. The prevalence is even higher among Indian women, with around 50% of women having low hemoglobin levels. Numerous studies conducted in India found that poor eating habits (not eating enough fruits, vitamin C, and legumes such as and beans and peas) and lack of access to healthcare are the main causes for such a high prevalence of anemia among women. Iron supplementation programs have not been successful in decreasing anemia in India. One reason for anemia being so common in both developed and developing countries could be that anemia is difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms are non-specific in the mild early stages. Studies suggest that more than 50% of people with anemia are not aware that they have the condition. Another reason could be due to the high prevalence of conditions that can cause anemia, such as CKD. In people with CKD, anemia arises due to kidney damage lowering the production of hormones that direct hemoglobin production. Anemia with CKD can be difficult to manage, as treatment of it can lead to other serious complications such as heart disease. As anemia can often be the indicator that there are more serious underlying illnesses, it is very important to improve disease awareness and obtain an accurate diagnosis of its cause.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataFor more insight and data, visit the GlobalData Report Store – Hospital Management is part of GlobalData Plc.
Related Reports
- GlobalData (2017). EpiCast Report: Chronic Kidney Disease – Epidemiology Forecast to 2026, December 2017, GDHCER175-17
- GlobalData (2018). Epidemiology and Market Size Database.