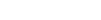Largest Hospitals in Japan by Bed Size 2021
Japan provides universal health coverage, with its statutory health insurance system (SHIS) covering 98.3% of the population and the remaining 1.7% being covered through the public social assistance programme for impoverished people.
The SHIS comprises more than 1,400 employment-based insurance plans covering approximately 59% of the population, the residence-based insurance plans provided by each of Japan’s 47 prefectures for all unemployed individuals aged below 74, and the government-sponsored insurance for the elderly people aged 75 and above.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Japan had more than 8,300 hospitals, with approximately 1.6 million beds, in 2021. The majority of the hospitals are private non-profit hospitals while 15% of them are public hospitals owned by the national government, prefectures and municipalities.
Hospital Management lists Japan’s top ten largest hospitals based on bed size, using GlobalData’s research.
1. Fujita Medical University Hospital – 1,376 beds
The Fujita Medical University Hospital is the biggest general hospital in Japan, with 1,376 beds.
Located in Toyoake, Aichi Prefecture, the multi-speciality teaching hospital has 1,325 general acute care and 51 psychiatric beds. The hospital annually performs more than 13,500 surgeries, and its emergency centre serves more than 25,000 patients a year.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataFujita Medical University Hospital provides advanced inpatient medical care in a wide range of specialities and is especially renowned for cancer and cardiovascular treatment, as well as neurosurgery and organ transplants.
2. Kyushu University Hospital – 1,275 beds
The 1,275-bed Kyushu University Hospital, located in Fukuoka, Kyushu Island, is the second biggest general hospital in Japan.
The multi-speciality teaching hospital has 37 medical and 12 dental departments. It provided inpatient medical care to 375,686 patients in 2021.
In addition, Kyushu University Beppu Hospital, the branch hospital, located in Beppu City, Oita Prefecture, has six medical departments and 140 acute care beds.
3. University of Tokyo Hospital – 1,226 beds
The University of Tokyo Hospital, located in Bunkyo City, Tokyo, is a multi-speciality teaching hospital with 1,226 beds, including 1,178 general acute care and 48 psychiatric beds.
The general medical and surgical facility has as many as 36 clinical divisions and departments, covering a comprehensive range of specialities such as cardiovascular, respiratory medicine, dermatology and neuropsychiatry.
The University of Tokyo Hospital performs more than 11,000 surgeries a year. It is renowned for gastrointestinal (GI), orthopaedic, spinal, and paediatric surgeries, as well as different types of organ transplantation.
4. St. Marianna Medical University Hospital – 1,200 beds
St. Marianna Medical University Hospital, located in Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture, is a multi-speciality teaching hospital with 1,200 beds.
It is the biggest among the four hospitals run by St Marianna University School of Medicine, which was founded in 1971. The remaining three hospitals of the university include the St. Marianna University Toyoko Hospital, St Marianna University Yokohama City Seibu Hospital and the Kawasaki Municipal Tama Hospital.
St Marianna Medical University Hospital has been operational since 1974. It has 31 clinical departments and is equipped with advanced systems to provide state-of-the-art medical care in a wide range of specialities.
5. Dokkyo Medical University Hospital – 1,195 beds
The Dokkyo Medical University Hospital, located in Kitakobayashi, Mibu, Shimotsuga, Tochigi, has 1,195 beds.
The multi-speciality teaching hospital provides inpatient medical care in a wide range of specialities, from diagnostic and generalist medicine to plastic and reconstructive surgery.
The Dokkyo Medical University was established in 1973. The 923-bed Saitama Medical Center in Koshigaya and the 199-bed Nikko Medical Center in Nikko City are also affiliated with the university.
6. Tokyo Women’s Medical University Hospital – 1,193 beds
Tokyo Women’s Medical University Hospital, located in Shinjuku, has 1,193 medical/surgical and intensive care beds.
Affiliated with the Tokyo Women’s Medical University School of Medicine, the multi-speciality teaching hospital has been operational since 1908.
The hospital has 50 clinical departments and performs more than 10,000 surgeries a year. It is known for performing one of the highest numbers of robot-assisted surgeries in Japan.
7. Tohoku University Hospital – 1,193beds
The Tohoku University Hospital, located in Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture, in Japan’s Tohoku Region, also has a total of 1,193 beds.
It is designated as an advanced treatment hospital by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW). Tohoku University Hospital was also one of the first teaching hospitals in the country to be accredited as a clinical research core hospital under the Medical Care Act of 1948.
Tohoku University Hospital is renowned for transplanting organs, such as the heart, lung, kidney, liver, intestine and pancreas.
8. Kawasaki Medical School Hospital – 1,182 beds
The Kawasaki Medical School Hospital, located in Kurashiki, Okayama, has 1,182 medical/surgical and intensive care beds.
Established in December 1973, it is the oldest and biggest of the two university hospitals run by Kawasaki Gakuen, a medical educational group based in Okayama. The other hospital operated by the group is the 647-bed Kawasaki Medical School General Medical Center, which opened in December 2016.
Kawasaki Medical School Hospital is designated as an advanced treatment and AIDS treatment core hospital, as well as a disaster centre hospital. It was also designated as a cancer core hospital by MHLW in 2008.
9. Kurashiki Central Hospital – 1,172 beds
The Kurashiki Central Hospital of Ohara HealthCare Foundation, located in Kurashiki, Okayama, is a multi-speciality teaching hospital having 1,172 beds, including 1,157 general acute care beds and five psychiatric and ten infectious disease beds.
The hospital has 37 clinical departments and provides a wide range of specialities, from gastroenterology and hepatology to general internal and critical care medicine.
Kurashiki Central Hospital provided medical care to more than 620,000 outpatients and 340,000 inpatients in 2021. The hospital also performs over 11,000 surgeries a year.
10. Iwate Medical University Hospital – 1,166 beds
The Iwate Medical University Hospital is a 1,166-bed teaching hospital located in Uchimaru, Morioka, Iwate.
The hospital has 47 clinical departments and provides inpatient care, with 1,088 medical/surgical and 78 psychiatric beds.
Iwate Medical University Hospital is designated as a hub hospital for cancer and dental care and AIDS treatment in the Iwate Prefecture of Japan. It is also home to the Iwate Prefectural Advanced Critical Care and Emergency Center and the Memorial Heart Center specialising in advanced cardiovascular treatment in the region.