Diabetes is one of the major non-communicable diseases globally. There are an estimated 450 million people with diabetes aged 20-79 years, including both diagnosed and undiagnosed cases. Undiagnosed diabetes is a major concern, as it often creates an additional socio-economic burden on a country’s healthcare system.
GlobalData epidemiologists forecast an increase in the diagnosed prevalent cases of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in the seven major markets (7MM) of the US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the UK, and Japan in the next decade, most notably in the US and the 5EU of France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK.
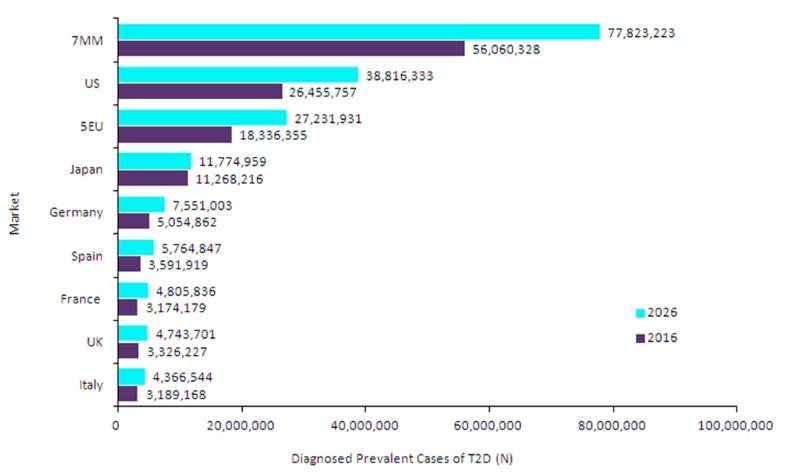
Figure 1 presents the expected changes in the 7MM from 2016 to 2026 in adults aged 20 years and older.
Figure 1: 7MM, Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of T2D, Men and Women, Ages ≥20 Years, 2016–2026. Source: GlobalData

Also known as non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, T2D is a chronic disorder that results from the body’s inability to make use of available insulin. This causes a buildup of glucose in the body.
T2D constitutes approximately 90%-95% of all diabetes cases worldwide, while type 1 diabetes (T1D) and gestational diabetes make up the remaining 5%-10%.
Among adult patients, T2D is expected to make up at least 95% of all diabetes cases. It is one of the most common non-communicable diseases and is an escalating public health problem globally. Poorly managed diabetes leads to serious complications such as heart attacks, strokes, kidney failures, leg amputations, vision loss, and nerve damage. Diabetes also increases the risk of fetal death and other complications during pregnancy.
In GlobalData’s T2D epidemiological analysis report 'EpiCast: Type 2 Diabetes – Epidemiology Forecast to 2026', GlobalData epidemiologists forecast that the diagnosed prevalent cases of T2D in the 7MM will increase from 56,060,328 cases in 2016 to 77,823,223 cases in 2026, with an annual growth rate (AGR) of 3.88% during the forecast period. The US will have the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases of T2D among the 7MM throughout the forecast period, while Italy will have the lowest.
In 2016, the US accounted for 47.19% of the diagnosed prevalent cases of T2D in the 7MM, with 26,455,757 cases. There were 18,336,355 cases in the 5EU in 2016, or 32.71% of the diagnosed prevalent cases, while Japan had 11,268,216 diagnosed prevalent cases, accounting for 20.10% of the diagnosed prevalent cases in the 7MM.
The growth in the prevalent cases of T2D in all these markets can be attributed to an increase in the prevalence of risk factors associated with the condition, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and dietary habits, along with changes in population demographics.
Related Reports
• GlobalData (2017). EpiCast Report: Type 2 Diabetes – Epidemiology Forecast to 2026, July 2017, GDHCER154-17
• GlobalData (2017). EpiCast Model: Type 2 Diabetes – Epidemiology Forecast to 2026, July 2017, GDHCEM154-17
• GlobalData (July 2017). PharmaPoint: Type 2 Diabetes – Global Drug Forecast and Market Analysis to 2026, GDHC152PIDR



